Lung Pain
09
July
2021
Pain or is it
Did you know that your lungs don’t have nerve receptors! They are the cells that are responsible for transporting pain impulses from an injured organ or area in your body to your brain. So, there is a great misconception about lung pain.
What might appear to you as lung pain might be related to muscles, asthma, the lining surrounding the lungs (pleura), or even the outer surface of the heart.
Lung Anatomy
Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. They are present within the thoracic cavity of your chest. They are a pair of air-filled, spongy organs with the left lung is smaller than the left one. There is a quite good reason for the size difference which is to provide a space for the heart. Both of you lung have a mass of 1.3kg or 2.9 lb.
Once you inhale, the air passes through your nose, pharynx, larynx, and then to that cartilaginous ringed tube, the trachea or also known as the windpipe. Through its tubular branches, known as bronchi, the trachea transports breathed air into the lungs. These bronchi divide further into smaller and smaller branches that are the bronchioles this continues until they are no longer capable of being seen by the naked eye.
The bronchioles finally finish into alveolar ducts that lead to the alveolar sacs (alveoli). The alveoli are clusters of small air sacs where the gaseous exchange takes place. The walls of the respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts are likewise covered with alveoli. The lungs have about 2,400 kilometers or 1,500 miles of airways and 300 to 500 million alveoli between them. Each lung is encased in a pleural sac containing pleural fluid, which allows the inner and outer walls of the lung to glide past each other without much contact while breathing. The lobes of each lung are thus divided by this sac. There are three lobes in the right lung and two in the left. The lungs' front and exterior sides are in contact with the ribs.
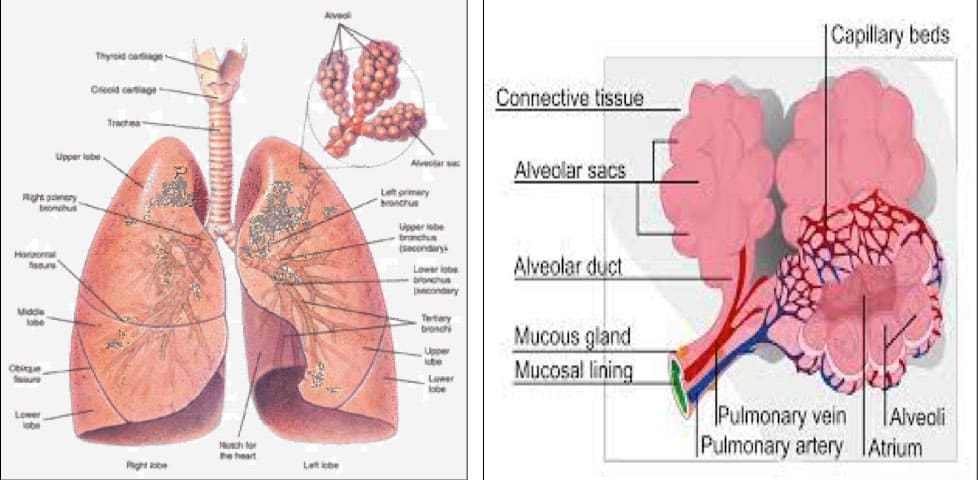
Now you might wonder how the gas goes from those sacs into the blood (gaseous exchange). This could be more understood when you know how your lungs are supplied with blood.
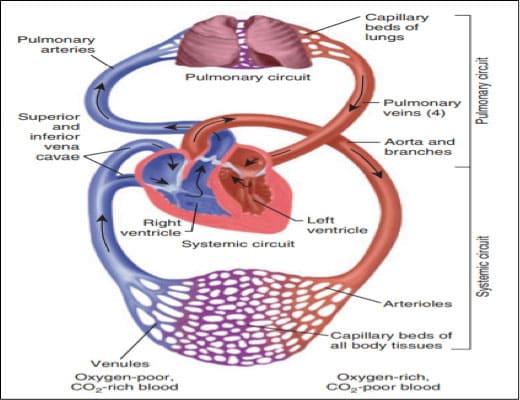
The lungs' primary function is gas exchange, which demands the use of blood from the pulmonary circulation. This blood supply has two main roles the first one is to carry blood rich in carbon dioxide to the lungs and simultaneously to carry blood rich in oxygen from the lungs to the heart by the erythrocytes, or red blood cells.
The pulmonary artery is the largest blood vessel coming from the heart to the lungs. This artery carries blood rich in carbon dioxide, this artery branches into arterioles and then many times until it ends up like a capillary surrounding the alveoli creating what is known as the respiratory membrane. At the level of alveoli and the capillary oxygen will diffuse from the air sac through the respiratory membrane to the blood capillary whereas carbon dioxide will diffuse from the blood capillary toward the air sac. This is the process of gaseous exchange in the lungs. This is your body's supply of oxygen.
The oxygenated blood will end up in the pulmonary vein which is transported to your heart and finally to your organs by systematic circulation.
Back to the pain
Call it what you like, lung pain or chest pain. The most important thing is where and how you sense the pain. There are different reasons for lung pain; these reasons could be related to pulmonary problems, muscles pain, or heart problems.
Pulmonary related problems
Airway restriction or partial airway blocking is a key feature of obstructive lung disorders.
This obstructive disorder is related to many various diseases such as COPD or Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This occurs when the alveolar cells lose their elastic property and over-expand as a result when you are exhaling some of the air will be trapped in your lungs. The symptoms are difficulty breathing out and thus shortness of breath. Chronic cough, wheezing and mucus production could also be common symptoms of COPD.
The major cause is cigarette smoke or any other chemical inhalant that can cause lung irritation.
Asthma belongs to obstructive disorder causes. Asthma is when the lungs' air passages suffer from inflammation and start to spasm. As a result, there will be difficulty in breathing generally shortness of breath, frequent cough, tiredness, pressure in the chest, and wheezing just like COPD. The symptoms might vary between different individuals. One could have one symptom and another individual would be having all. Even the asthma attacks might vary. Sometimes, it could be mild and other times, it could be very severe. The leading reasons for asthma could be an allergy, air pollution, and viral or bacterial infections.
In addition to the obstructive disorder, there is the chronic restrictive lung disorder that is determined by the limitation of the presence of lung tissues involved in respiration. This is due to long-term infection of the lung which causes lung fibrosis where the lung tissues are replaced by fibrous connective tissues. Symptoms of this disease include a chronic cough, chest discomfort, trouble breathing, and exhaustion.
Fibrosis is caused by different diseases such as autoimmune disease, black lung disease, or the Coal workers' pneumoconiosis (CWP) due to long-term exposure to coal dust, or in rare cases severe reaction to a certain medication.
It is not necessary to have a chronic disorder when there is lung pain. It could be due to infections starting from pneumonia to bronchitis. These infections are accompanied by heavy cough, fever, and sudden weight loss. This can be caused by viral, bacterial, or believe it or not fungal infection.
Cancers are another reason for lung pain. Cancer is the building up of extra cells that become tumors eventually. Cancer causes pain in the tumor area itself and it is associated with other symptoms such as coughing out blood in advanced stages and weight loss.
A serious cause of pain is Pulmonary Embolism that is due to the formation of a small blood clot in the leg that shatters into pieces and travels along with the blood circulation to the lungs. Once in the lungs, the emboli will cause sudden chest pain that becomes worse and difficulty in breathing. Coughing, fast heart rate, shortness of breath, swelling, and tenderness in the calf are also other symptoms.
Sometimes the pleural membrane that holds your lungs gets infected. This would be known as pleuritis. The symptoms are a little bit different from the earlier disorders. You might feel a sharp pain when taking a deep breath. Pleuritis is caused sometimes by health conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmune diseases. Moreover, it could be due to the infection of a virus or bacteria.
Heart pain
Sometimes the pain is due to a certain heart condition where the blood flow could be obstructed, which can cause feelings of heaviness, pressure, or tension in the center or on the left side.
Muscles pain
Not all of your lung pains are necessarily due to lung infection some of them could be related to other reasons like muscles pain Fibromyalgia for example. Despite the lack of apparent muscle or joint damage or inflammation, fibromyalgia is a condition that produces widespread musculoskeletal discomfort. Tenderness in the chest wall area is a common symptom of fibromyalgia, and it can be misinterpreted as lung discomfort or pain. This disease could be caused by emotional or physical incidents, infections, or simply inherited.
Costochondritis is a muscle chest pain condition that frequently involves inflammation where the ribs meet the sternum. People with this disease frequently experience stinging, burning, or sharp pain on the outside of their chest.
Finally, the pain could be from acid reflux that causes a burning sensation or even digestive tract problems.
How can you be diagnosed?
It is very necessary to take care of your health, no matter what the reason is, when you feel any pain you should consider checking a doctor.
The doctor will try to identify the source of pain by checking your medical history along with the physical examination and diagnostic tests.
The diagnostic tests will start from blood test to X-ray to ECG (for excluding the heart), to spirometry for pulmonary diagnosis.
How could the treatment be?
The treatment would vary depending on the results of the diagnostic tests. Some treatments might be non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID), specific antibiotics, or even thoracotomy can be performed in treating serious lung cases or to attain a lung tissue biopsy.
How to keep yourself protected?
Always take care of your health, stay away from smoking and secondhand smoking, take the necessary vaccines when applicable and try to keep up a healthy mode of life.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from pain, call us today on (469) 562 4188 to book an appointment with our expert doctors.